Gum Disease Symptoms and Treatment: Everything You Need to Know
Maintaining good oral health is more than just keeping your teeth white—it’s also about taking care of your gums. Healthy gums are the foundation of a strong smile, but when neglected, they can develop serious problems like gum disease. Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is one of the most common dental issues worldwide, yet it often goes unnoticed until it becomes severe.
In this article, we’ll explain the main symptoms of gum disease, its causes, and the best treatment options available to restore your gum health.
What Is Gum Disease?
Gum disease is an infection and inflammation of the tissues that surround and support your teeth. It usually starts as gingivitis (the mildest form) and can progress to periodontitis, which can cause tooth loss if left untreated.
This condition occurs when bacteria in plaque—a sticky film that constantly forms on your teeth—begin to irritate and damage the gums. Over time, this leads to swelling, bleeding, and eventually destruction of the bone that supports your teeth.
Common Symptoms of Gum Disease
Recognizing the early warning signs of gum disease is key to preventing long-term damage. Here are the most common symptoms you should watch for:
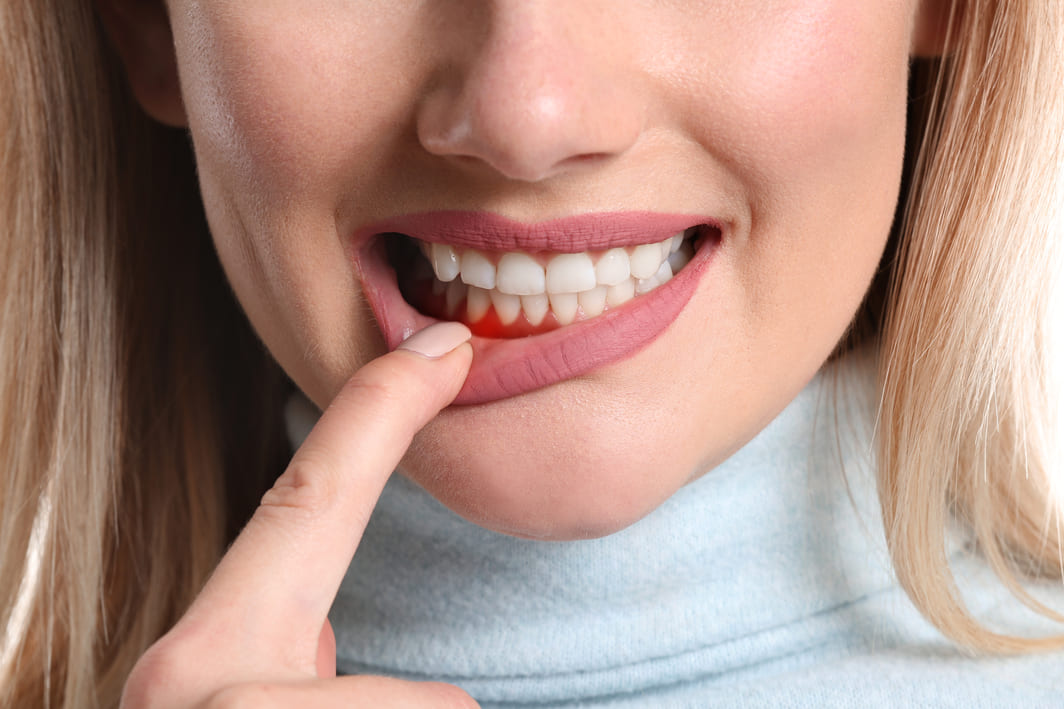
1. Red, Swollen, or Tender Gums
Healthy gums should look pink and firm. If your gums appear red, puffy, or sore, this is an early sign of inflammation.
2. Bleeding While Brushing or Flossing
A little bleeding might seem harmless, but it’s often the first noticeable sign of gum disease. If you notice pink on your toothbrush or dental floss, it’s time to take action.
3. Persistent Bad Breath
Chronic bad breath (halitosis) can result from bacteria trapped below the gum line, releasing toxins and odors.
4. Receding Gums
As gum disease progresses, your gums may start to pull away from your teeth, making your teeth look longer than before. This is a serious sign that needs dental attention.
5. Loose or Shifting Teeth
Advanced gum disease weakens the bone and tissues that hold teeth in place, leading to loose or moving teeth.
6. Pain While Chewing
Discomfort when eating or biting can be caused by gum inflammation or infection spreading to deeper tissues.
7. Pus Between Gums and Teeth
If you notice pus or an abscess around your gums, it indicates a severe infection that needs immediate dental treatment.
What Causes Gum Disease?
Several factors can contribute to the development of gum disease. The most common include:
- Poor oral hygiene: Infrequent brushing and flossing allow plaque buildup.
- Smoking or tobacco use: This weakens gum tissue and slows healing.
- Hormonal changes: Pregnancy, menopause, and menstruation can make gums more sensitive.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can increase infection risk.
- Genetic factors: Some people are more prone to gum disease due to their genetics.
- Certain medications: Drugs that reduce saliva flow can increase plaque buildup.
- Poor nutrition: Lack of vitamins, especially vitamin C, can weaken gum health.
Stages of Gum Disease
There are two main stages of gum disease:
1. Gingivitis
This is the earliest and most reversible stage. Symptoms include mild bleeding, redness, and swelling. With proper brushing, flossing, and dental cleaning, gingivitis can be completely cured.
2. Periodontitis
If gingivitis is not treated, it can progress to periodontitis. At this stage, the inner layer of the gum and bone pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that become infected. Periodontitis can lead to permanent bone loss and tooth loss.
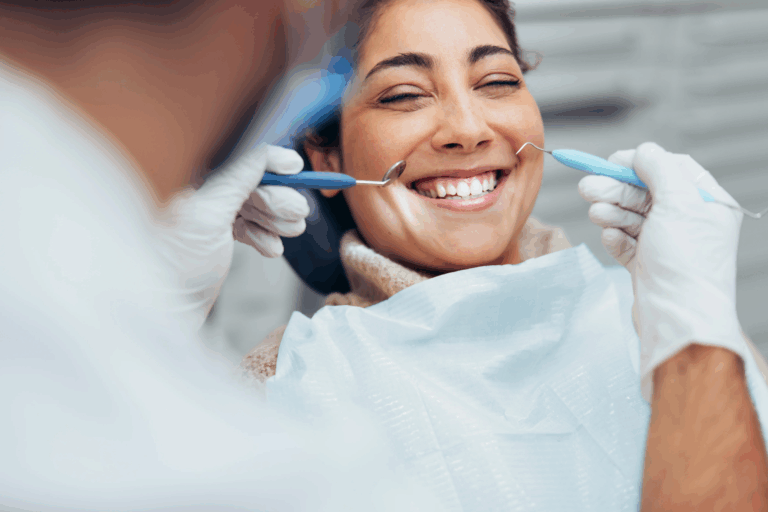
How Gum Disease Is Diagnosed
Dentists use several methods to detect gum disease, such as:
- Visual examination of your gums for redness, swelling, or bleeding.
- Probing: Using a small instrument to measure the depth of pockets around your teeth.
- Dental X-rays: These help check for bone loss beneath the gum line.
Early diagnosis is essential to prevent the disease from spreading or causing irreversible damage.
Treatment Options for Gum Disease
Treatment depends on the severity of your condition. The goal is to control the infection, reduce inflammation, and prevent further damage.
1. Professional Dental Cleaning
For early-stage gum disease, your dentist may recommend a thorough cleaning to remove plaque and tartar. This process, known as scaling and polishing, helps eliminate bacteria from above and below the gum line.
2. Scaling and Root Planing
This deep-cleaning procedure involves removing plaque and tartar from below the gums (scaling) and smoothing the root surfaces (planing) to help gums reattach to the teeth. It’s typically done under local anesthesia.
3. Medications
Antibiotic mouth rinses, gels, or oral tablets may be prescribed to kill bacteria and reduce infection.
4. Surgical Treatments
In advanced cases, surgical options may be required, such as:
- Flap surgery: Lifting the gums to clean deeper areas and repositioning them afterward.
- Bone grafting: Rebuilding bone lost due to periodontitis.
- Soft tissue grafts: Replacing receding gum tissue with grafts from other parts of the mouth.
5. Lifestyle Changes
Improving your daily oral care routine is crucial to recovery. Brush twice a day, floss daily, eat a balanced diet, and quit smoking to support healing.
Preventing Gum Disease
Prevention is always better than treatment. Here are a few tips to keep your gums healthy:
- Brush twice a day using fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss daily to remove food particles between teeth.
- Use an antibacterial mouthwash to reduce plaque buildup.
- Visit your dentist regularly for checkups and professional cleaning.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamin C, calcium, and antioxidants.
- Avoid tobacco in any form.
By maintaining these habits, you can prevent gum disease and enjoy lifelong oral health.
Why Treating Gum Disease Is So Important
Ignoring gum disease doesn’t just affect your mouth—it can impact your overall health. Research has shown links between gum disease and systemic conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections.
Inflamed gums allow bacteria to enter the bloodstream, increasing inflammation throughout the body. Treating gum disease early helps protect not only your teeth but also your overall well-being.
When to See a Dentist
You should schedule a dental appointment if you notice any of the following:
- Gums that bleed easily.
- Persistent bad breath.
- Pain or swelling in your gums.
- Receding gums or loose teeth.
Even if you’re not experiencing pain, early detection can make a huge difference in treatment outcomes.
Conclusion
Gum disease is a common but preventable condition that affects millions of people worldwide. By understanding its symptoms and knowing how to treat it, you can take charge of your oral health. Regular dental visits, proper hygiene, and healthy lifestyle choices are your best defense against gum problems.
Remember, your smile starts with healthy gums—take care of them, and they’ll take care of you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can gum disease be cured completely?
Yes, early-stage gum disease (gingivitis) can be fully reversed with good oral hygiene and professional cleaning. However, advanced periodontitis can only be managed, not completely cured.
2. How long does it take to treat gum disease?
Treatment duration depends on the severity. Mild gingivitis can improve in a few weeks, while severe periodontitis may require months of treatment and regular follow-ups.
3. Does gum disease cause bad breath?
Yes, bacteria that accumulate in the mouth due to gum disease release unpleasant odors, leading to chronic bad breath.
4. Can I treat gum disease at home?
You can manage early signs through better oral hygiene, but professional dental care is necessary to fully remove plaque and tartar buildup.
5. How often should I visit the dentist to prevent gum disease?
It’s recommended to visit your dentist every 6 months for regular cleaning and checkups. If you’re prone to gum problems, more frequent visits may be advised.